Sean's Notes
Powered by 🌱Roam GardenCritical Thinking
see also qualitative research
What is CriticalThinking?
The aim of critical thinking is to try to maintain an objective position. When you think critically, you weigh up all sides of an argument and evaluate its strengths and weaknesses. So, critical thinking entails: actively seeking all sides of an argument, testing the soundness of the claims made, as well as testing the soundness of the evidence used to support the claims.
Critical thinking is not:
- restating a claim that has been made
- describing an event
- challenging peoples’ worth as you engage with their work
- criticizing someone or what they do (which is made from a personal, judgemental position).
While CriticalAnalysis AnalyticalThinking requires you to examine ideas, evaluate them against what you already know and make decisions about their merit, CriticalReflection ()SyntheticThinking) requires you to synthesise different perspectives (whether from other people or literature) to help explain, justify or challenge what you have encountered in your own or other people’s practice.
BloomsTaxonomy | Bloom’s taxonomy can provide a useful way of conceptualising higher-order thinking and learning. The six intellectual domains...
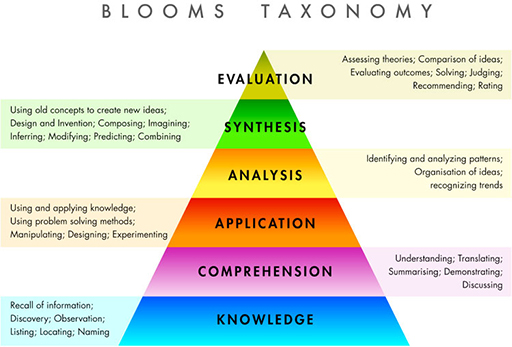
Higher-order intellectual domains, descriptions and associated keywords
Knowledge | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling information, fundamental facts and terms, as well as discovery, through observing and locating. // MyNote: Generally this is better defined as "Information" at least by myself and as referenced in Organizing Knowledge: Taxonomies, Knowledge and Organizational Effectiveness.
Who?
What?
Find
Define
Recall
Comprehension | Demonstrate Understanding of facts and ideas by organising, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptors and stating main ideas.
Compare
Contrast
Explain
Discuss
Application Solve problems in new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different or new way. // a type of Understanding
Plan
Build
Experiment
Design
Solve
Interview
Analysis Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalisations. AnalyticalThinking
Dissect
Examine
Infer
Compare
Contrast
Synthesis - Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. SyntheticThinking
Compose
Construct
Create
Design
Develop
Theorise
Elaborate
Formulate
Evaluation This is also denoted as ‘critical evaluation’, often used to emphasize the depth of evaluation required. You will be required to present and defend opinions by making judgements about information, the validity of ideas or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Also SyntheticThinking - Wisdom
Compare
Justify
Prove
Disprove
Deduct
Tags:: Idea Development big-ideas
MyThought - CriticalThinking is a (the?) Process of evaluating and creating information, knowledge, understanding, and wisdom from Data. Following this process helps you create big-ideas and is an effective process of Idea-Development. Critical thinkings 'output' is Understanding and is a type of SyntheticThinking . The information that is inputted (through fact-finding & the knowledge we already have) are the bits of data that AnalyticalThinking is concerned with.
In a way CriticalThinking a process of first 'doing' AnalyticalThinking then 'doing. SyntheticThinking
Referenced in
Notes on Mastery
Now that you’ve collected a large database of recipes and started applying them, you should begin to develop some contextual understanding of when to use which recipes.
Mastery the “Adventure to Excellence” & The Ultimate Growth Skill
Critical Thinking* - expanding upon what we've learned so far.
Notes on Mastery
Study the craft of those who are truly craftsmen — who are brilliant and nuanced at what they do. Peel back the layers until you begin to see how the sausage is made — why did they make the decisions they made in what they were doing? Why that ordering of decisions? aka Critical Thinking